How Is Euglena Both Plant And Animal Like
Table of Contents:
- Classification of Euglena
- Euglena Diagram
- Morphology and Anatomy
- Diet
- Reproduction
Euglena is a blazon of euglenoid. Euglenoids are unicellular microorganisms, that have a flexible body. They possess the characteristic features of plants and animals. Euglena has plastids and performs photosynthesis in light, but moves effectually in search of food using its flagellum at dark. There are around thou species of Euglena found. They are found in freshwater, saltwater, marshes and too in moist soil.
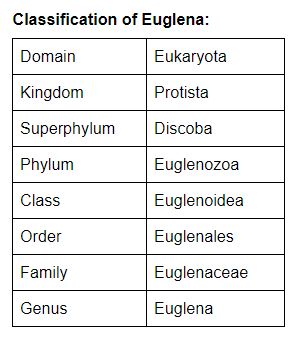
Euglena Classification
Euglena is a genus of euglenoids. The classification of Euglena is contentious. They are kept in the phylum Euglenozoa or in the phylum Euglenophyta with algae due to the presence of chlorophyll. Since all the species of Euglena do not incorporate chloroplasts, they are kept in the phylum Euglenozoa. The class Kinetoplasteae in the phylum Euglenozoa contains not-photosynthetic flagellates known every bit Trypanosomes, which are parasitic and crusade serious diseases in humans such equally African sleeping sickness, leishmaniasis.
Euglena Structure with Diagram and Characteristics

Morphology and Anatomy
- Euglena has an elongated cell measuring fifteen-500 micrometres
- Mostly green in colour due to the presence of chlorophyll paint
- Some of the species of euglena contain carotenoid pigments, which give it distinct colour similar red
- Euglena is unicellular having one nucleus
- Euglena lacks the cellulose jail cell wall present in a plant prison cell
- There is a presence of a flexible outer membrane known every bit a pellicle, which supports the plasma membrane. The pellicle is equanimous of a proteinaceous strip and supporting microtubules. The pellicle gives flexibility to the jail cell and an ability to contract and change its shape
- A thin plasma membrane is nowadays, which encloses the cytoplasm and cell organelles
- Information technology contains a contractile vacuole which removes excess water
- There is inward pocket almost the base of flagella called a reservoir, where contractile vacuole dispels backlog water
- Diverse prison cell organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi bodies are nowadays
Diet
- Euglena contains chloroplast having chlorophyll. These chloroplasts accept the green algal origin and seemed to have acquired due to endosymbiotic relationship
- They perform photosynthesis, just also require other organic nutrients and vitamins such as vitamin B12
- Some of the photosynthetic euglenoids lose their chlorophyll when they abound in the dark and obtain nutrients heterotrophically from organic thing
- Some species of Euglena are besides heterotrophs
- The heterotrophic species of Euglena either absorb organic compounds from the surrounding water or engulf bacteria and protists by phagocytosis within the food vacuoles
- The chloroplast of Euglena contains pyrenoids, which is used to synthesize paramylon, a ꞵ-ane, iii polymer of glucose
- Food is stored in the form of paramylon, which provides energy when at that place is no light
- Some species of Euglena produce an alkaloid known as euglenophycin, which is found to kill fishes
- Euglena is cultivated for large scale production in some countries like Japan for commercial product of paramylon. Some species of Euglena have shown to contain vitamin E (⍺-tocopherol) and high content of astaxanthin
Locomotion and Phototaxis move
- It has an eyespot also known every bit stigma, that contains photoreceptors for detection of light and involved in phototaxis
- Lite detected past the eyespot is focused on paraflagellar body
- I or ii flagella are present, which help in locomotion
- Mostly ii flagella are nowadays, that originates from a small reservoir inside the cell
- I curt flagellum is present, which does non protrude out of the cell, the long flagellum is used for swimming
Reproduction
- Euglena reproduces asexually past binary fission, they divide longitudinally
- Their lifecycle consists of a free-swimming and a non-motile stage
- It produces thick-walled protective cyst that can withstand unfavourable conditions, this is feature of a non-motile stage
- Some euglenoids brand reproductive cyst under unfavourable conditions. Many Euglenoids assemble together, leave their flagella and get enclosed in a gelatinous substance. Private Euglena produces reproductive cyst, which produces daughter cells by binary fission. Under favourable conditions, these daughter cells go flagellated and come out of the mass. This is known as the palmelloid stage of the lifecycle.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Euglena a plant or animal?
Euglena is a genus of unicellular, flagellated microorganisms. They possess characteristics of both plants and animals but are neither placed in the kingdom Plantae nor Animalia. They vest to the kingdom Protista.
Are Euglena prokaryotic or eukaryotic?
Euglena is a genus of eukaryotic, unicellular and flagellated microorganisms. They comprise a well-divers nucleus and other cellular organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, chloroplasts and Golgi bodies, etc.
Where is Euglena establish?
They are found in freshwater, saltwater, marshes and likewise in moist soil.
Why Euglena is known every bit mixotrophs?
Euglena has chloroplasts and performs photosynthesis in light, but moves around in search of nutrient using its flagellum at dark. Some of the photosynthetic euglenoids lose their chlorophyll when they grow in the dark and obtain nutrients heterotrophically from organic matter. The heterotrophic species of Euglena either absorb organic compounds from the surrounding h2o or engulf bacteria and protists by phagocytosis inside the food vacuoles.
Since they show both autotrophic and heterotrophic style of nutrition, they are known equally mixotrophic.
What are euglenoids?
Euglenoids are the best-known flagellates of the phylum Euglenozoa. Euglenoids have an outer poly peptide layer called the pellicle. They are unicellular and biflagellate. Examples of euglenoids are Euglena, Trachelomonas, etc.
Likewise Check:
NEET Flashcards: The Living World
NEET Flashcards: Biological Classification
NEET Flashcards: Jail cell The Unit Of Life
NEET Flashcards: Prison cell Cycle And Jail cell Sectionalisation
NEET Flashcards: Reproduction In Organisms
Recommended Video:
Source: https://byjus.com/neet/euglena-structure-and-classification/
Posted by: nelsonhadvaid.blogspot.com

0 Response to "How Is Euglena Both Plant And Animal Like"
Post a Comment